The Coupled Model Intercomparison Project (CMIP) coordinates climate model simulations worldwide under the World Climate Research Program (WCRP). CMIP's goal is to better understand and predict past, present, and future climate change in a multi-model context. In order to compare model results, CMIP is developing standards for simulations, data formats, and evaluation algorithms, among other things. This will give climate researchers the ability to directly share, compare, and evaluate their findings with each other. The data products of the sixth phase of CMIP (CMIP6, Eyring et al. 2016, GMD, 9, 1937-1958, 2016, doi:10.5194/gmd-9-1937-2016) thus represent, in addition to observational data, an important source of robust and reliable climate information in the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change's (IPCC) Sixth Assessment Report. The scenario subproject of CMIP6, ScenarioMIP, involved a total of about 27 institutions worldwide with 32 to 38 (depending on the scenario) different models or model configurations (Tebaldi et al. 2021, Earth Syst. Dynam., 12, 253-293, 2021, doi:10.5194/esd-12-253-2021). The calculations for the German contributions to this were performed partly by DKRZ and mostly on DKRZ's high-performance computer Mistral.
The SSP Scenarios
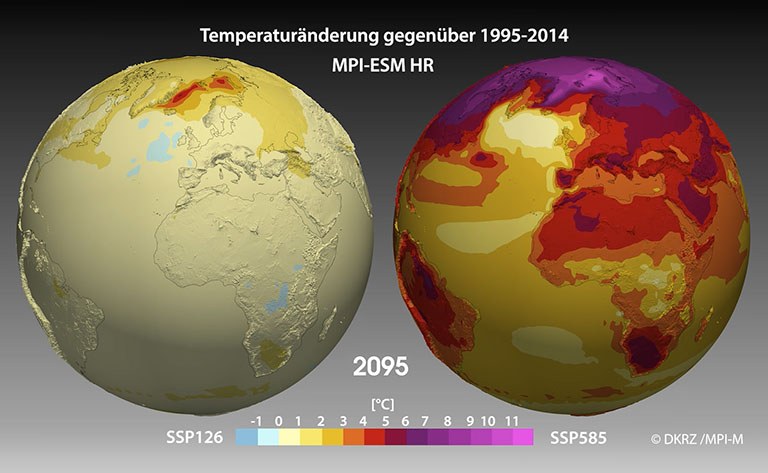
The SSP scenarios: A new set of climate scenarios, the so-called SSP scenarios (Shared Socioeconomic Pathways), has been developed in view of the 6th world climate assessment report. The new SSP scenarios have been improved in a variety of ways compared to the previously used RCP scenarios. Read more ...