Results
The extensive simulations, which were carried out with the Earth system model MPI-ESM with respect to the CMIP5 project and the IPCC AR5, are key to numerous scientific projects for the years to come. A total of more than 650 terabytes simulation data was produced. By presenting a selection of visualizations for different key climate variables and for the different scenarios, we show the possible bandwidth of future climate changes.
https://www.dkrz.de/en/communication/climate-simulations/cmip5-ipcc-ar5/ergebnisse
https://www.dkrz.de/@@site-logo/dkrz.svg
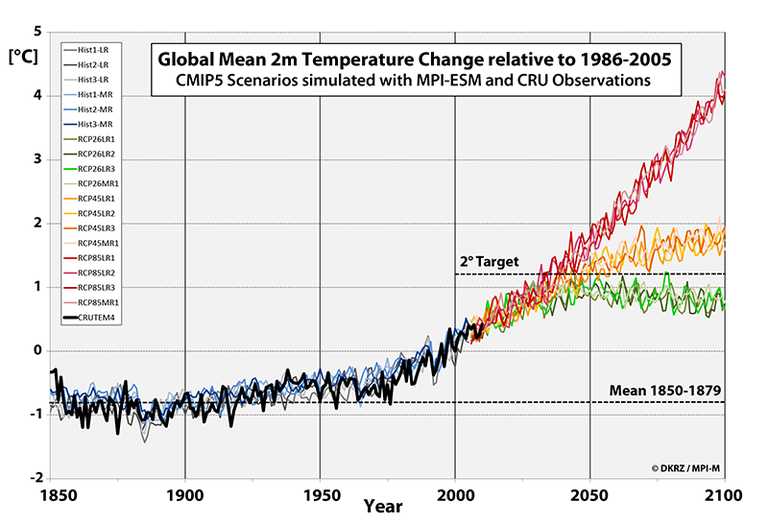
Global Mean Temperature
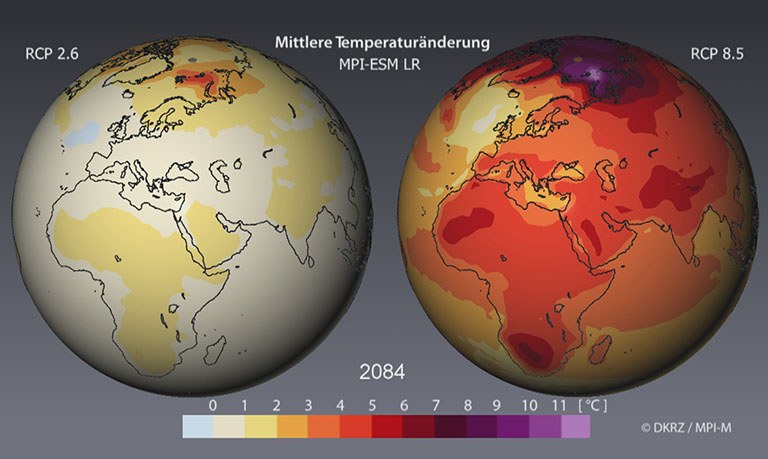
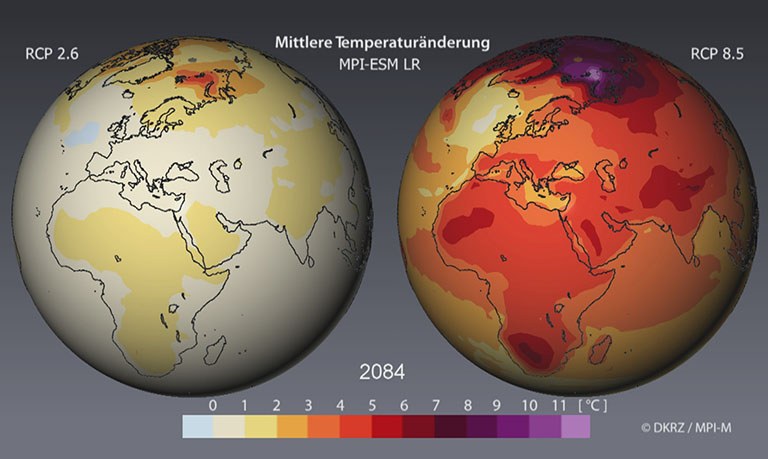
The air temperature (2m-temperature) is one of the most important climate parameters that is directly affected by heightened radiation from increased greenhouse gas concentrations.
2m Temperature
The simulated changes in the 2m temperature due to the changed conditions prescribed by the scenarios have varying degrees of prevalence depending on their geographic situation.
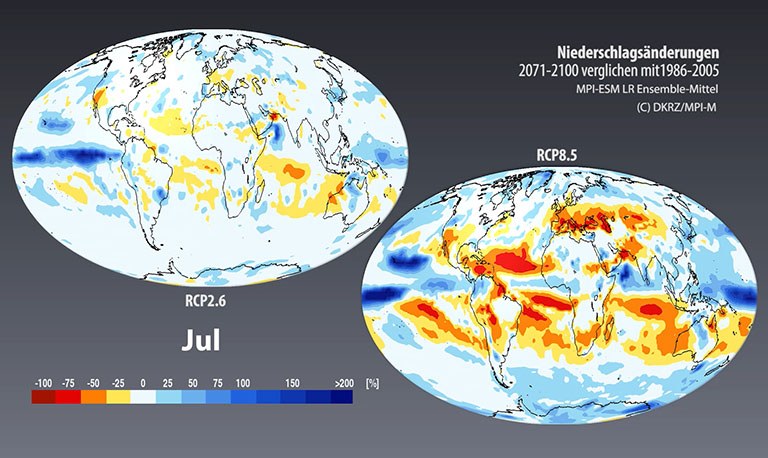
Precipitation
Due to the temperature increase, the water cycle is intensified, causing an increase in global mean precipitation as well. At the same time, however, there is a redistribution causing some areas to receive more precipitation and others less, depending on the season.
Sea Ice
Sea ice and snow are quite important factors in the climate system.
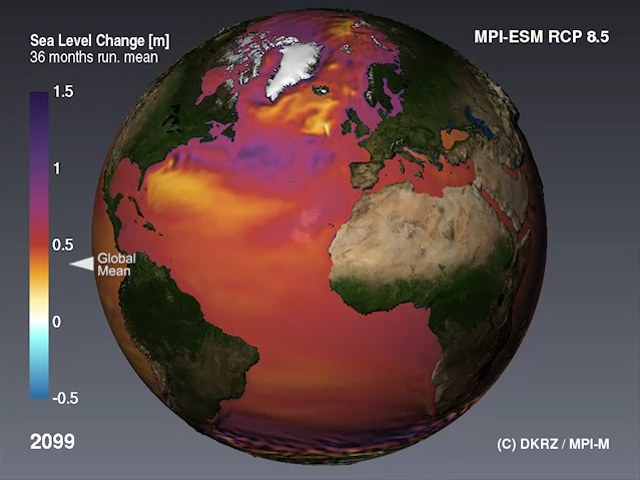
Sea Level
With increased temperatures, water will expand and therefore cause the sea level to rise. Changes in air temperature cause a further change in the water cycle and ocean currents. Together, these factors exhibit different regional changes in sea levels.
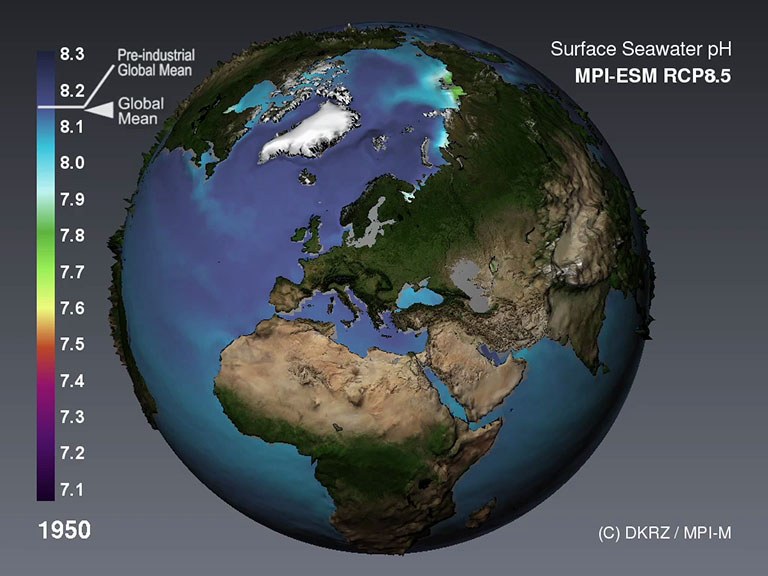
Ocean Acidification
The ocean’s surface water is home to countless organisms which have thrived in mostly constant chemical conditions for over two million years. With the begin of the industrialization, these conditions have started to change.
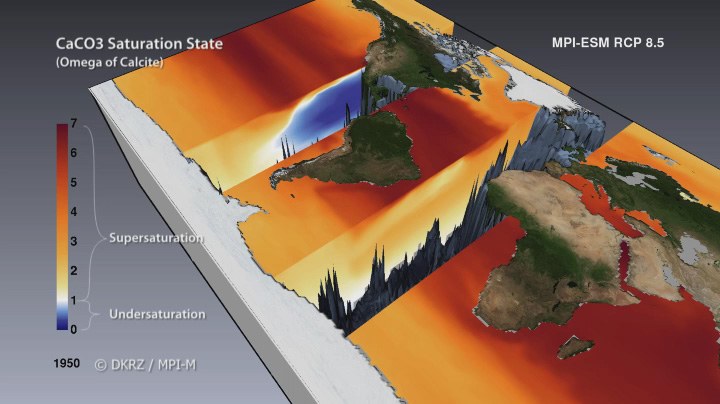
Carbonate in the Ocean
As a consequence of ocean acidification, a rather important building block to oceanic life could become scarce, namely, calcium carbonate.